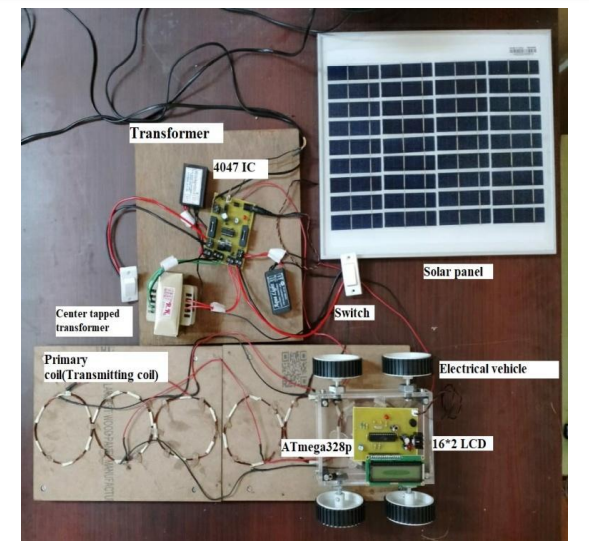
Solar Wireless Electric Vehicle Charging System":-
- Atmega Controller
- Battery
- Voltage Sensor
- LCD Display
- Transformer
- Regulator Circuitry
- Transmitter and Receiver Coils
- Vehicle Body
- Wheels
- Switches
- LED’s
- PCB Board
- Resistors
- Capacitors
- Transistors
- Cables and Connectors
Description:-
The Number Of Electric Vehicles On The Road Today Is Steadily Increasing. In Addition To The Environmental Advantages, Electric Vehicles Have Demonstrated Usefulness In Lowering Travel Expenses By Substituting Electricity For Fuel, Which Is Significantly Less Expensive. However, There Are 2 Significant Drawbacks To Electric Vehicles:
- It Takes A Long Time To Charge—between One And Three Hours.
- Charging Facilities In Rural And Outlying Regions Are Not Powered.
Here, We Create An Innovative, One-of-a-kind EV Charging System That Addresses Both Of These Issues. The Advantages Of Using This EV Charging Setup Are As Follows:
- Vehicles Can Be Wirelessly Charged Without Using Wires.
- No Need To Stop Because The Vehicle Charges While It Is In Motion.
- No External Power Source Is Required Because Solar Power Will Power The Charging System.
- Road Coils Built In To Prevent Deterioration
Solar Panels, Batteries, Transformers, Regulator Circuits, Copper Coils, Ac To Dc Converters, Atmega Controllers, And Lcd Displays Are All Used In The System's Construction. The Method Shows How Electric Vehicles May Be Charged While Travelling Down The Road, Doing Away With The Need To Pull Over.
Through The Use Of A Charge Controller, The Battery Is Powered By The Solar Panel. DC Electricity Is Fed Into And Stored By The Battery. Now That The DC Power Is Ready For Transmission, AC Conversion Is Required. Here, We're Using A Transformer For This.
A Transformer Is Used To Convert The Power To AC, And Regulator Circuitry Is Used To Regulate It. The Copper Coils That Are Utilized For Wireless Energy Transmission Are Now Powered By This Energy.
Additionally, A Copper Coil Is Installed Underneath The Electric Car. Energy Is Transmitted From The Transmitter Coil To The EV Coil When The Car Is Driven Across The Coils.
Please Take Note That The Energy Is Still Induced Into This Coil As DC Current. To Enable Use In Charging The EV Battery, We Now Convert This Back To DC.
To Convert It Back To Dc Current, We Employ Circuitry For AC To DC Conversion. The Input Voltage Is Now Also Measured By An Atmega Microprocessor, And The Results Are Shown On An LCD Screen.
As A Result, The Technology Shows How A Wireless Solar-powered Charging System For Electric Vehicles May Be Included Into The Road.
Block Diagram:
Important Notes:-
If You Looking For A Ready-Made Projects, Kindly Comments Below.
We Will Provide You DIY Kits With Notebook To Submit In Your College Or School Or University.
Trending Posts This Month:-
System For Monitoring Plant Moisture | Electrical Engineering Projects Ideas
Smart Home Burglar Alarm Systems | Final Year Electrical Engineering Projects
Final Year Project Based On "Automatic Smoke Detector Alarm"
Solved Examples Problems On Star-Delta Transformation Or Conversion
Solved problem based on Norton’s Theorem
Solved Problem Based On Superposition Theorem
Example Solved Problems Based On Thevenin Theorem Circuit
Tricky Solutions For Equivalent Series-parallel Resistance Problems With Examples
Solved Problem Based On Maximum Power Transfer Theorem
Mesh-analysis - Loop-analysis -Maxwell's Current Analysis | Electrical
Delta To Star Transformation Or Delta To Star Conversion and Its Formulas
Superposition Theorem And Method Of Solving Superposition Theorem
Reading Problems Based On Superposition Theorem Example & Solved Formula's





18 comments:
While this technology could significantly reduce the hassle of charging, it's still important for EV owners to consider having an EV home charger installation. Charging at home remains the most convenient and cost-effective option, especially for those who don't always have access to public charging stations. As advancements continue, perhaps we’ll see solar-powered home chargers become a reality too!
EV Charger Installation with solar system in Sydney, Australia
Best EV Chargers in Sydney, Australia
EV Charger Installation in Sydney, Australia
hi
An onboard computer in EV chargers could enhance diagnostics, offering real-time insights into battery health and vehicle performance.
Home EV charger could become as essential as home appliances in the future. Advancements in charging technology and energy efficiency will shape their adoption.
EV charger have the potential to be as common as gas stations, ensuring seamless charging accessibility as the world shifts to electric mobility.
With smart charging and off-peak usage incentives, EV charger can be integrated without overwhelming the power grid.
Higher electricity demand from EV charger might impact prices, but time-of-use rates and smart charging can help control costs.
Are you unsure what kind of charger you need? That’s where we come in. At The EV Man, we offer comprehensive consultation and expert advice.
Electric vehicles are revolutionizing transportation with cleaner, quieter, and more energy-efficient mobility.
yess
Very informative post! We at Hezire Technologies specialize in top-quality car chargers in UAE, offering reliable and safe charging solutions for every smartphone and gadget.
I’ve heard a lot of positive feedback about Voltanio and its innovative charging solutions.
That’s such an impressive concept! I completely agree that combining solar power with EV charger installation is a game-changer for sustainable transport. The idea of charging vehicles wirelessly while in motion is especially exciting and could really push renewable tech forward. Companies like KDEC are also keeping an eye on innovations like this, which shows how quickly the industry is advancing. Thanks for the post!
Also, how do you think this kind of system could be adapted for everyday city use?
Really interesting take on wireless EV charging through solar energy. As this tech evolves, the role of reliable automotive electrical wire becomes even more critical behind the scenes. Smart energy transfer still depends on solid electrical infrastructure to stay efficient and safe.
This explains the power flow in a really straightforward way, especially how the battery stores the solar energy before conversion. Many people focus on green tech but still worry about the ev charger install cost in Australia, so practical details like this help make the idea feel more realistic. Could this system work for regular home setups?
Post a Comment