In This Subject Topic, We Will Understand The "Types Of Earthing Used In Electrical System".
The Following Earth Types Must Be Included In The Instrument Earthing System:
Electrical Earthing, Sometimes Known As Protective Earthing (PE) Or Dirty Earthing, Reference Earth (RE), Another Name For Instrument Earthing.
Earthing That Is Inherently Safe: To Prevent Electric Shock To Humans, Electrical Equipment, And The Power System, Electrical Earthing Is Employed.
How Is An Electrical Earthing Performed?
Field Instrument Cable Armor Must End At The Cable Gland. Cable Glands Are Where The Armor Of Single And Multicore Cables That Are Headed To Junction Boxes Should End. The Earth Stud Bolt Only Has To Be Connected To The Closest Steel Structure If The Junction Box Is Made Of Metal. The Earth Stud Bolt Will Be Found At The Metal Gland Plates That Are In Direct Contact With The Cable Gland If The Junction Box Is Built Of Non-metal Material.
When Single Or Multicore Cables Enter Or Exit The Marshalling And System Cabinet, They Must Be Terminated And Linked To A Bus Bar Located Within The Cabinet. Every Bus Bar Within The Cabinet Will Be Linked To A Grounding Dispatcher By A 35 Mm Square Cable, Which Is Often Yellow-striped And Green In Color. This Grounding Dispatcher Will Gather All Connections From Each Bus Bar And Then Use A 70 Mm Sq Cable To Link It To A General Electrical Earth Loop (To The Structure Steel). The Earth Bus Bar Is Typically Utilized And Is ½" In Width And ¼" In Height. It Is Composed Of Copper.
Earthly Instrument: Instrument Earthing Generally States That Each Individual Shield And Overall Shield Of A Single Or Multiple Pair Of Cables Must Be Isolated From Electrical Earthing And Terminated At A Separate Bus Bar. Since This Instrument Earth Serves As The Reference Point Of The Instrument Loop—the Ground Of The Instrument's Internal Electric Circuit—it Is Also Commonly Referred To As The Reference Earth.
Within The Instrument Enclosure, The Ground Terminal Block Or Earth Should Be Where The Individual Shield (Drain Wire) Of A Single Pair Cable Terminates.
Each Analog Single-pair Cable Shield That Enters The Junction Box Must Be Terminated At The Terminal Block. Each Shield From The Digital Single-pair Cable Entering The Junction Box Needs To Be Terminated At The Terminal Block, Jumper Out, And Connected To The Bus Bar.
Every Single Shield From A Multi-pair Cable That Enters The Junction Box Needs To Be Terminated To Match The Terminal Block Of Every Single-pair Cable.
The Terminal Block Or Bus Bar Is Where The Overall Shield From The Multi-pair Analog Cable Entering The Junction Box Should Terminate (The Overall Shield Of The Analog Cable Does Not Have A Pair With The Shield From The Single-pair Cable). The Overall Shield From The Multiple Pairs Of Digital Cables Entering The Junction Box Needs To End At The Bus Bar.
At The Marshalling Cabinet, Each Individual And Combined Shield (Screen) From Several Pairs Of Cables Must Be Terminated Into The Appropriate Instrument Earth Bus Bar.
The Instrument Bus Bar Will Be Linked Via A 25 mmsq Green-yellow Stripped Wire To The Grounding Dispatcher. It Will Be Connected To The Main Instrument Earth Loop From The Grounding Dispatcher By A 70 mmsq Green-yellow Stripped Wire.
Earthing That Is Inherently Safe: The Same Procedure That Was Previously Described For Instrument Earth Should Be Followed For The Isolation And Termination Of Is Field Cable Shields (Screens) At Field Devices, Junction Boxes, And Marshalling Cabinets. Nevertheless, Each Termination Of The Multi-pair Cable's Overall Shield (Screen) For Is Signals That Flows To The Marshalling Cabinet Must Be Attached To Its Is Bus Bar Separately. This Cable's Individual Shield, Or Screen, Will Be Directly Terminated To A Galvanic Isolator Before Being Linked To The Appropriate Is Bus Bar.
Following The Installation Of The Instrument Earthing System:-
The Following Maximum Resistance Limitations Must Be Met.
- To Enable The Safe Grounding Of The Sub-normal Current At The Steel Structure, This Resistance Is Reduced To The Lowest Practicable Value.
- Not More Than 0.5 Ohms Separates The Instrument Earth Bus Bars From The Grounding Dispatcher.
- Between The Frame Of The Electrical Equipment And The Closest Nearby Stud Earth On The Structural Steel, Not More Than One Ohm.
- Not More Than 0.5 Ohm Separates The Grounding Dispatcher From The Fundamentally Safe Installation.
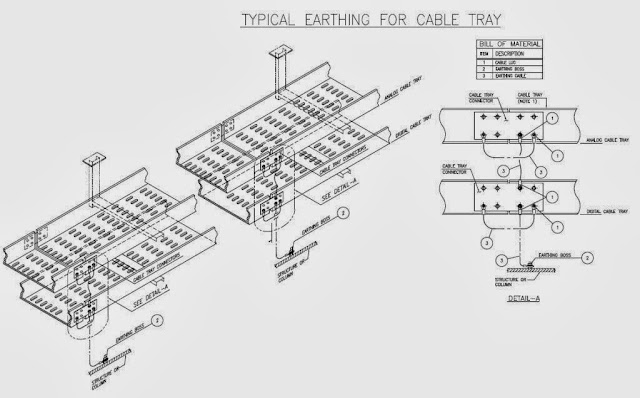
Typical Earthing For Cable Tray:-
Typical Earthing For Digital Signal Junction Box.
Typical Earthing For Analog Signal Junction Box.
Attention:-
Kindly Note That To View More Jobs Post , You Can Also Click On The Arrow "Right/Older Post" Or "Left/Pervious Post " Next To "HOME" Icons.







No comments:
Post a Comment